The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the Earth Observation Satellite EOS-8 and the small satellite SR-0 DEMOSAT aboard the SSLV-D3 rocket from the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota on Friday morning. The mission marks the third and final developmental flight of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
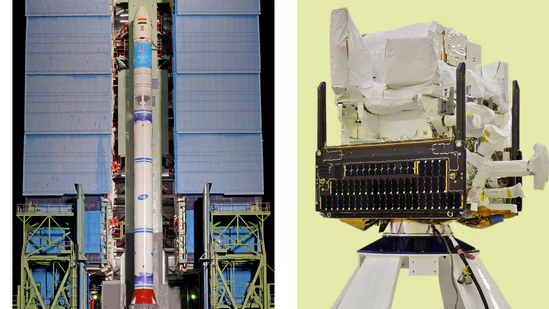
The EOS-8 satellite, weighing 175.5 kg, will operate in a circular orbit at an altitude of 475 km above the Earth. The primary objectives of the EOS-8 mission include the design and development of microsatellites with advanced capabilities.EOS-8 carries three key payloads: the Electro-Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR), the Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry Payload (GNSS-R), and the SIC UV Dosimeter. The EOIR is intended for satellite-based surveillance, disaster monitoring, and environmental observation.
GNSS-R will demonstrate remote sensing capabilities for analyzing sea surface winds, estimating soil moisture, and detecting floods. The SIC UV Dosimeter is designed to monitor ultraviolet radiation, with a specific focus on the upcoming Gaganyaan mission.SR-0 DEMOSAT, a passenger satellite, was also successfully deployed and will function alongside EOS-8 in their shared orbit.